Cell death and tumor cells
Crosstalk between the extrinsic and the intrinsic apoptosis pathway
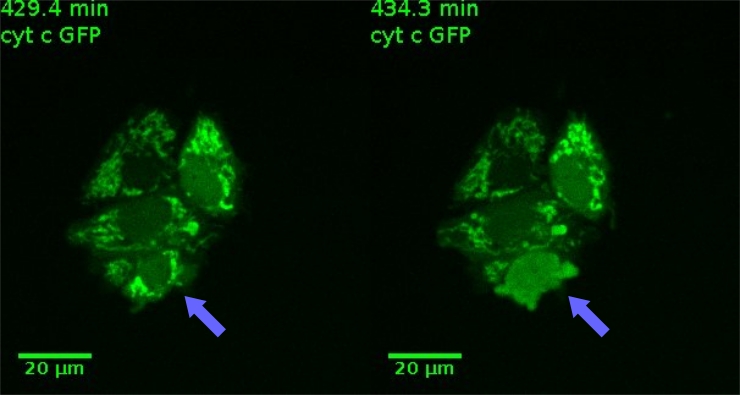
While death ligands of the TNF family induce apoptosis predominantly via the so-called extrinsic pathway, i.e. direct caspase activation at the receptor complex, chemotherapeutic drugs and radiation activate the intrinsic apoptosis pathway proceeding via activation of the Bcl-2 family and the permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane. However, interactions between the extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathway are known and play an important role in the amplification and fine tuning of cell death induction. Our research group has a major interest in how signals via TNF receptors amplify the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway induced by various drugs. Primarily we focus on the interaction and activation of the so-called Bcl-2 interactome.
Thiazolides and tumor therapy
Most types of tumors develop mechanisms, which render them resistant to various therapeutic approaches and drugs. Thus, drugs targeting specific resistance mechanisms may allow to sensitize tumor cells for cell death induction. We are investigating in this context the mechanism of thiazolide-induced cell death in colorectal tumor cells. Thiazolides are drugs used in the treatment of intestinal infections. However, thiazolides also promote apoptosis induction on tumor cells, such as colorectal tumor cells. Glutathion-S-transferases (GST) are detoxifying enzymes, which are generally overexpressed in tumor cells and render them resistant to chemotherapeutic drugs. Surprisingly, thiazolide-induced apoptosis induction is dependent on GST enzymatic activity, thus revealing GST as an „Achilles’ heel“ in thiazolide-induced cell death. We are investigating the mechanisms of thiazolide-induced apoptosis in tumor cells and the therapeutic potential in cancer therapy.
Selected publications
Brockmann, Bluwstein, Kögel, May, Marx, Tschan, and Brunner. Thiazolides promote apoptosis in colorectal tumor cells via MAP kinase-induced Bim and Puma activation. Cell Death Dis. 6:e1778. 2015
Brockmann A, Strittmatter T, May S, Stemmer K, Marx A, Brunner T. Structure-function relationship of thiazolide-induced apoptosis in colorectal tumor cells. ACS Chem Biol. 9(7):1520-7.
2014.
Sidler D, Brockmann A, Mueller J, Nachbur U, Corazza N, Renzulli P, Hemphill A, Brunner T. Thiazolide-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells is mediated via the Jun kinase-Bim axis and reveals glutathione-S-transferase P1 as Achilles’ heel. Oncogene. 31(37):4095-106. 2012
Schneider-Jakob S, Corazza N, Badmann N, Sidler D, Stuber-Roos R, Frese S, Tschan M, Brunner T. Synergistic induction of cell death in liver tumor cells by TRAIL and chemotherapeutic drugs via the BH3-only proteins Bim and Bid. Cell Death Dis. 1, e86. 2010
Corazza, N., Jakob, S, Schaer, C., Frese, S, Keogh, A., Stroka, D., Mueller, C., Schneider, P., and Brunner, T. TRAIL receptor-mediated JNK activation and Bim phosphorylation critically regulate Fas-mediated liver damage and lethality. J Clin Invest. 116:2493-9. 2006
